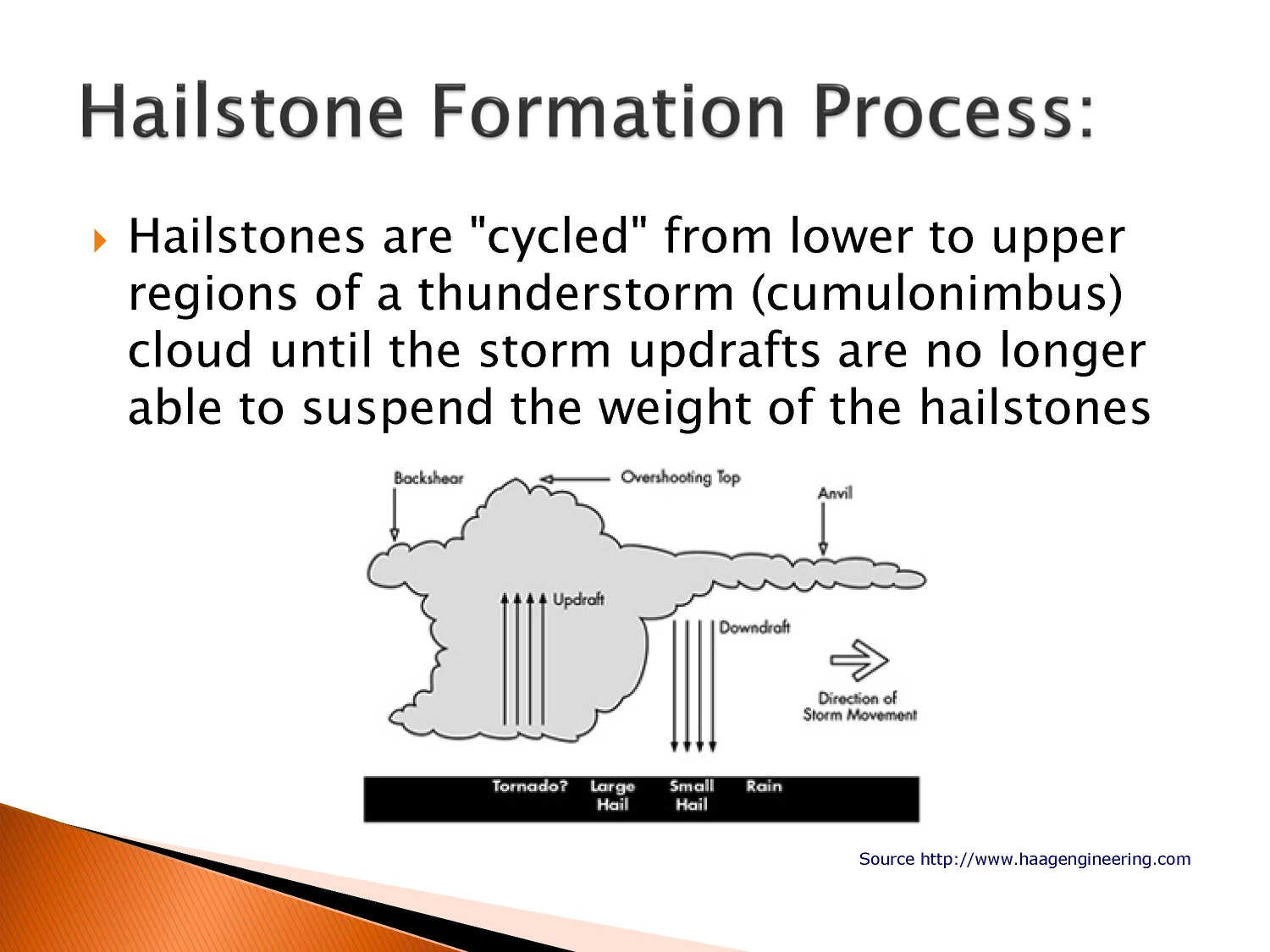
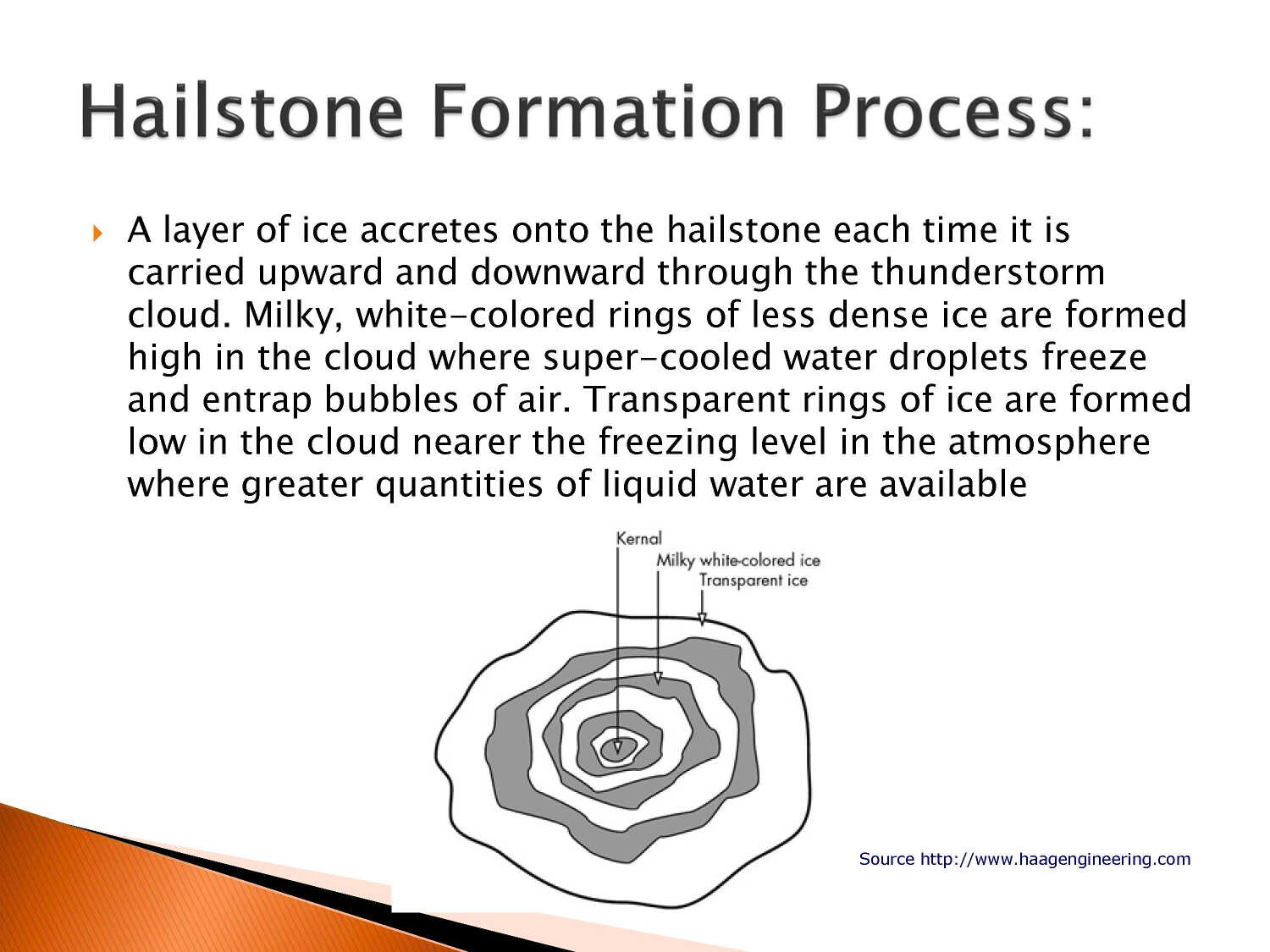
Defined as:
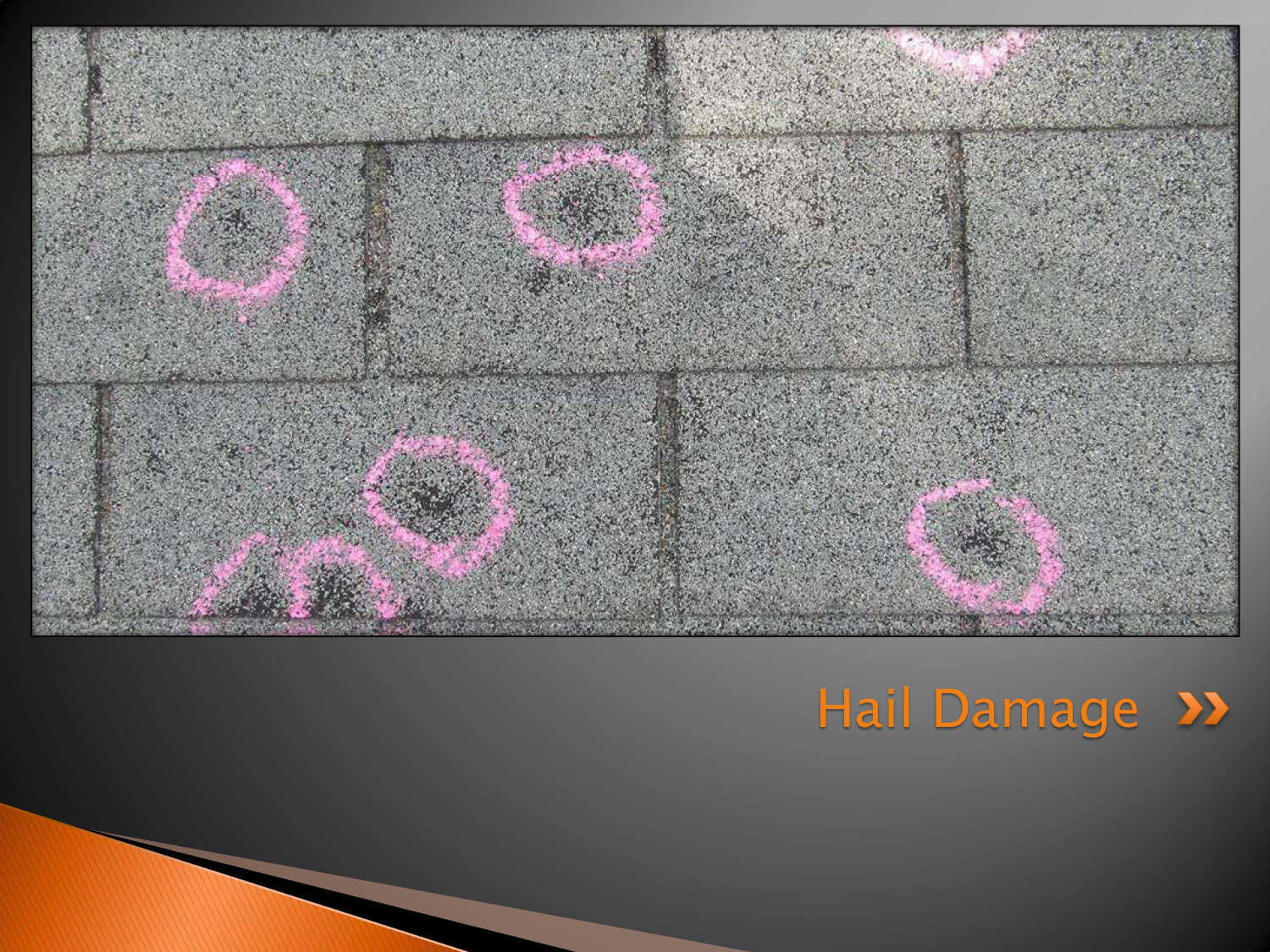
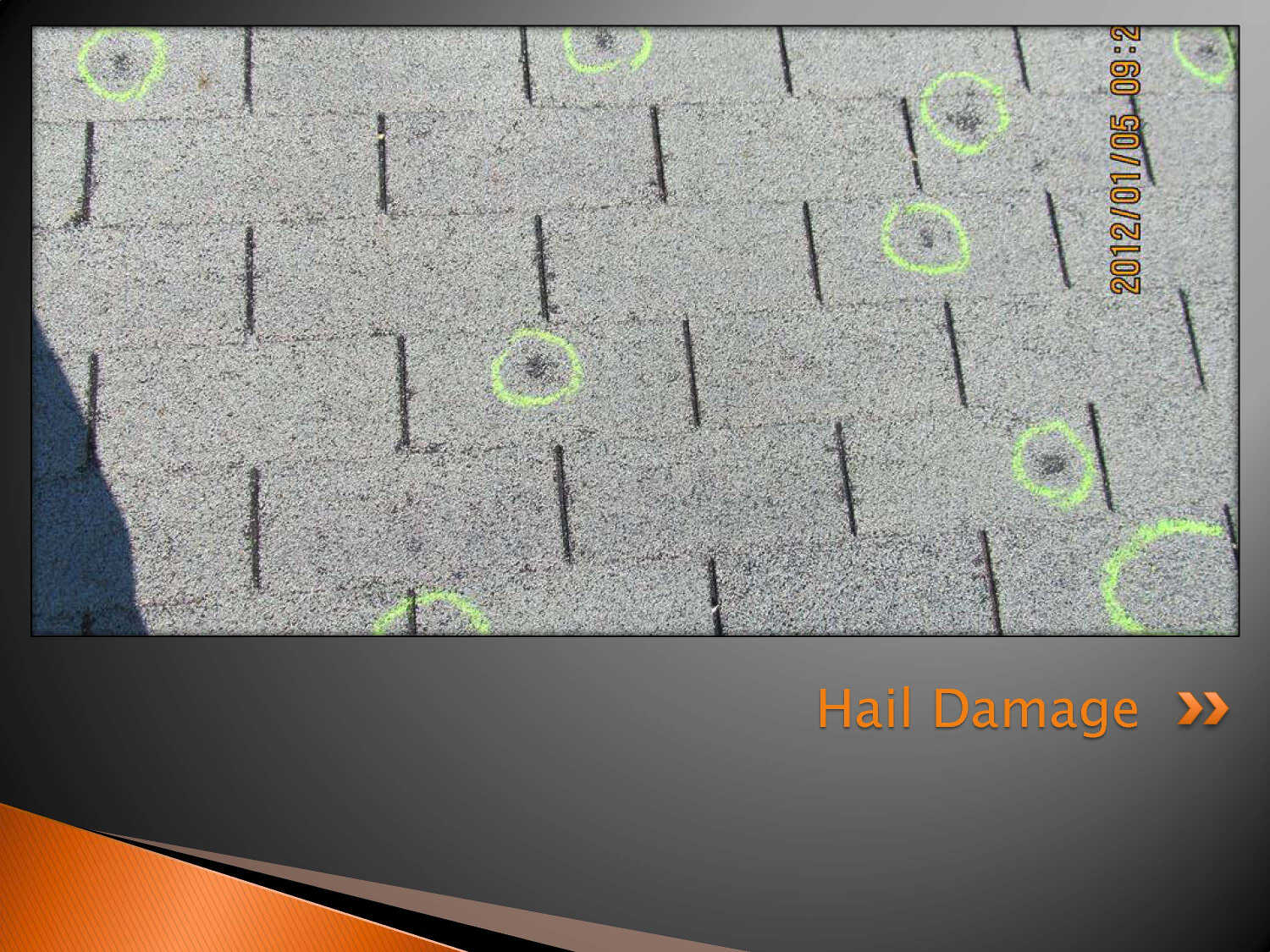
- Impact fracturing causing a reduction in the water shedding capabilities as a result of impact caused ruptures or fractures in the reinforcement mat.
- Impact damage causing a reduction in the expected long-term service life of the material as a result of asphalt exposure within well defined consistent patterns of impact marks.
Granule loss
Granule loss is not an automatic determination of Hail Damage
Many roofing professionals claim that granule loss following a hail storm constitutes roof replacement. Years of testing and research has proven that granule loss does not automatically result in hail damage and cannot be a determining factor when making a roof assessment. Granule loss within any weather related event is considered to be part of the natural aging process of a shingle. Tests have concluded that a hail and/or rain storm will remove a very small percentage of granules from an asphalt shingle.
Granules on a roof have four main purposes. They are: protection of the asphalt coating from UV light, providing coloring and beauty with multi colored granules, providing some fire resistance, and add to the aid of shingle packaging. Today’s shingles contain a finely ground dolomite powdered ground rock, that is applied to the asphalt for strength and density, thus providing a very good UV protector for areas of shingle tabs that have lost granules. Dolomite is a second layer of protection to the shingle from the UV light in the areas of missing granules.
1/2 (.50) Moth ball
FEW, IF ANY, ROOFS DAMAGED. Bushes and trees- leaves stripped; crops- damaged. Oxidation coatings on paint, wood, metal- spattered. Thin elastomeric coatings on polyurethane foam roofs- cracked or broken. Thin aluminum vents, fins on air conditioning units, lead sleeves on soil stacks, window screens, aluminum awnings- dented.
3/4 (.75) Penny
THRESHOLD SIZE FOR DAMAGE TO ROLL ROOFING AND DETERIORATED ASPHALT COMPOSITION SHINGLES, ESPECIALLY WHERE UNSUPPORTED. Painted wood surfaces, deteriorated gray-black slates (especially at corners)- chipped. Most aluminum vents, flashings, valleys, siding- dented.
1 (1.00) Quarter
THRESHOLD SIZE FOR DAMAGE TO MOST LIGHTWEIGHT ASPHALT COMPOSITIONSHINGLES. Thin and/or deteriorated wood shingles, shakes- occasionally punctured or cracked. Single-pane windows, thin skylight shells- cracked or broken.
1-1/4 (1.25) Half dollar
THRESHOLD SIZE FOR DAMAGE TO MOST HEAVY WEIGHT ASPHALT COMPOSITION SHINGLES, WOOD SHINGLES, AND OLDER MEDIUM SHAKES. Automobile body metal- dented; galvanized metal vents- dented. Older plastic skylights- cracked or broken.
1-1/2 (1.50) Walnut
THRESHOLD SIZE FOR DAMAGE TO CLAY TILE, SLATE, MEDIUM SHAKES, AND MODIFIED BITUMEN SINGLE-PLY MEMBRANES. Automobile body metal- extensive denting.
1-3/4 (1.75) Golf ball
THRESHOLD SIZE FOR DAMAGE TO HEAVY SHAKES AND CONCRETE TILES . Metal vents- caved in. Bare spots and blisters on deteriorated built-up roofs- bruised or punctured.
2 (2.00) Hen egg
THRESHOLD SIZE FOR DAMAGE TO JUMBO SHAKES, WELL-SUPPORTED UNBALLASTED BUILT-UP ROOFING, AND UNBALLASTED EPDM.
2-1/2 (2.50) Tennis Ball
THRESHOLD SIZE FOR DAMAGE TO WELL-SUPPORTED BALLASTED BUILT-UP ROOFING, BALLASTED EPDM, AND METAL PANELS.

Examples of Hail damage to Asphalt Shingles